Problem description:
Sort a linked list in O(n log n) time using constant space complexity.
1
2
3
4
| Example 1:
Input: 4->2->1->3
Output: 1->2->3->4
|
1
2
3
4
| Example 2:
Input: -1->5->3->4->0
Output: -1->0->3->4->5
|
Solution:
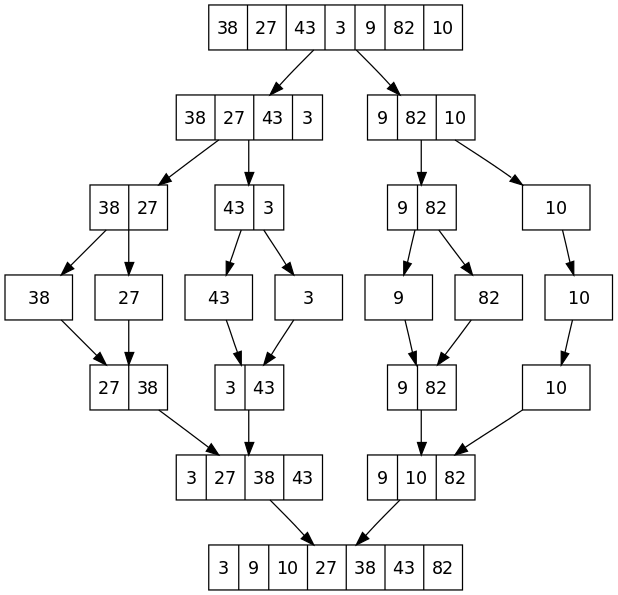
The description is asking for algorithm that runs within O(nlogn). Therefore, only quicksort, merge sort, heap sort can meet the requirement.
- First of all, we cut the list into half, the code is widely use, make sure to memorize it.
- Then we keep cut it into half, until there’s only one node left.
- Start merging the list and sort it.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) {
if(!head || !head->next) return head;
ListNode *prev= head, *slow= head, *fast= head;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next != NULL){
prev = slow;
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
prev->next = NULL;
ListNode* l1 = sortList(head);
ListNode* l2 = sortList(slow);
return merge(l1, l2);
}
ListNode* merge(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2){
if (!l1) return l2;
if (!l2) return l1;
if (l1->val < l2->val) {
l1->next = merge(l1->next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2->next = merge(l1, l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
};
|
time complexity: O(nlogn)
space complexity: O(logn), it’s the tree’s depth
reference:
https://goo.gl/uJF4wn
