778.Swim in Rising Water
Problem description:
You are given an n x n integer matrix grid where each value grid[i][j] represents the elevation at that point (i, j).
The rain starts to fall. At time t, the depth of the water everywhere is t. You can swim from a square to another 4-directionally adjacent square if and only if the elevation of both squares individually are at most t. You can swim infinite distances in zero time. Of course, you must stay within the boundaries of the grid during your swim.
Return the least time until you can reach the bottom right square (n - 1, n - 1) if you start at the top left square (0, 0).
Example 1:
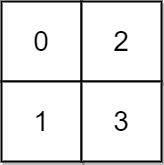
1 | Input: grid = [[0,2],[1,3]] |
Example 2:
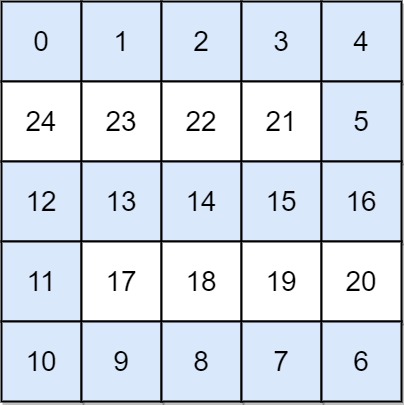
1 | Input: grid = [[0,1,2,3,4],[24,23,22,21,5],[12,13,14,15,16],[11,17,18,19,20],[10,9,8,7,6]] |
Constraints:
n == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= n <= 500 <= grid[i][j] < n2- Each value
grid[i][j]is unique.
Solution:
We want to find if could reach to last position
Use a heap to record that available neighbor
A visited set to
1 | class Solution: |
- Time Complexity:
O(N^2 log N). We may expandO(N^2)nodes, and each one requires `O(logN)` time to perform the heap operations. - Space Complexity:
O(N^2), the maximum size of the heap.
time complexity: $O()$
space complexity: $O()$
reference:
related problem: